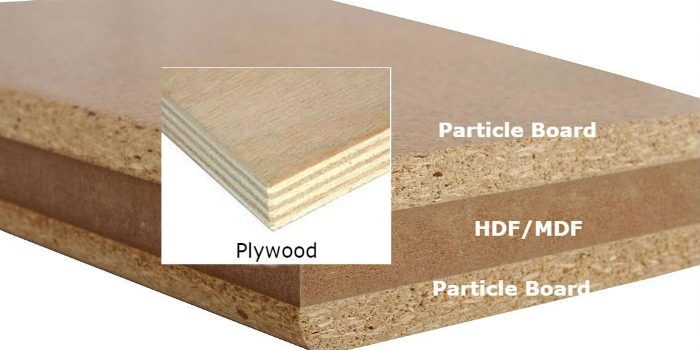
Engineered woods
1.Fiberboards
Medium Density Fiberboard (MDF)

MDF is a type of wooden material constituting of lignocellulosic fibers combined with resin and wax in the presence of high pressure and temperature. In the market, fiberboards are graded in terms of densities. Their making process sees variations of pressure and temperature resulting in different densities of the material. For example, HDF (High density Fiberboard) will require more pressure and temperature.
This type of Fiberboard lies between the High Density Fiberboard (HDF) and particle board. Particle board is the lowest density fiberboard. Moreover, MDF has no voids and is stronger in comparison to Particle board.
Advantages of MDF
- MDF has a smooth feel consistent on the entire material.
- MDF is less costly than Plywood.
- It makes use of wood residuals in their processing phase thereby enables more conservation of trees.
- For its finishing, painting is easier on MDF compared to typical wood as some colors won’t be suitable for it.
- MDF can be shaped to suit various designs. The consistent smooth nature of the material makes it easier to cut through using tools such as jigsaw and band saw.
- For Veneer, it is an excellent substrate.
- MDF is consistent in strength too.
Disadvantages of MDF
- Unless it is properly and completely sealed, MDF will soak up water, swell and break. To prevent this, use a suitable sealing product such as an oil-based primer.
- It is a heavy material compared to plywood.
- During cutting and sanding, it is advisable to use a particle mask. The reason behind this is MDF has formaldehyde which can cause irritation or allergy. Formaldehyde also increases chances of an individual getting cancer as it emits certain gases. With time, a piece of furniture made of MDF will have less of these substances. The US and UK government have established minimal content of formaldehyde in home furniture to be 0.11ppm and 0.07ppm respectively. For new furniture made of MDF, it is advisable to isolate it until its smell ends. Airflow should also be encouraged in the room to minimize exposure.
- Working on the edge of the MDF with screws may cause it to split. In addition to this, MDF are poor holders on screws and may subsequently strip from them.
- It is difficult to repair split or chipped MDF unlike solid wood
High Density Fiberboard (HDF)

HDF is made from wood fibers bond with resin under high pressure and temperature. It is harder and stronger than the Medium Density Fiberboard (MDF). This material can be found in various sizes with its density of about 900kg/m3. HDF can be applied to various areas such as doors, cupboards, flooring and other numerous house designs.
Advantages of HDF
- It has a smooth consistent feel.
- HDF is stronger than MDF and Particle board.
- It is cheaper than solid wood.
- Similarly to MDF, HDF is easy to cut.
- HDF is easy to paint on unlike solid wood.
Disadvantages of HDF
- Like MDF, HDF can be affected by water. It will swell and break if it not water resistant.
- HDF requires replacing after five years thus is not durable.
- HDF are poor holders on screws and may strip
Particle board

This is the fiberboard with the lowest density. Particle board can be used in furniture, wall paneling and flooring. More so, Particle board is the weakest of the fiberboards.
Advantages of Particle Board
- It is the cheapest of all fiberboards.
- It is less costly than solid wood.
- It possesses a smooth feel.
- Particle board has multiple varieties.
- Not all particle boards contain formaldehyde.
- Particle board is lighter in weight.
- It can hold screws more than MDF and HDF.
Disadvantages of Particle Board
- It gets deformed once saturated with water.
- It is the weakest of all the fiberboards.
- It the least durable type of fiberboard.
- Moisture has a big effect on it similarly like the other fiberboards.
- It is not meant for heavy loads due to its low strength.
2. Plywood

Plywood is a board of plies or sheets of real wood glued together. The arrangement of these sheets which have grains will determine the strength of the whole material. There are numerous instances where plywood is used for different purposes. Some of its applications are on floors, roofs, furniture which are custom built, walls and kitchen cabinets. Below are the types of plywood:
Hardwood plywood
This type of plywood has great strength and stiffness. With great impact resistance, hardwood plywood is used for wall structures. Although it will require finishing for a smooth attractive look, hardwood plywood can be used in making furniture. Hardwood plywood can be made from oak, mahogany, birch or maple.
Softwood plywood
Softwood plywood is a product derived from softwood trees such as fir, cedar and spruce. Softwood plywood is mostly used in furniture making whereas hardwood is applied in construction. Moreover, softwood plywood is less expensive than hardwood plywood but less durable than the latter.
Tropical plywood
This type of plywood is derived from tropical wood. It has a better strength and quality than softwood plywood. This has brought about an increase in its demand worldwide. There has also been an increase in its price as buyers search for reliable sources in Asia and Africa.
Advantages of plywood
- It possesses great uniform strength. By establishing an alternating pattern for the grains, plywood is able to gain uniform strength.
- It is available in several large sizes unlike solid wood.
- The layers of plywood can be altered to give both beauty and strength.
- In contrast to solid wood or real wood, plywood makes the most out of the raw material available. Its making assists in conserving trees.
- Depending on the type, plywood is a versatile material.
- Hardwood plywood lasts longer because of its great quality in strength. In general too, plywood is more durable than fiberboards (MDF,HDF and Particle board)
- Plywood costs cheaper than solid wood.
Disadvantages of plywood
- It is essential for a purchaser to buy water resistant plywood if its later use will expose it to wet conditions. This is because the layers may detach.
- One has to find a trustworthy source when buying the material. It is easy to tell the type of wood used on the outer layers but not the inner ones.
- Work has to be done on the edges of the plywood where the layers are observed. This is mostly the case when using plywood as a material for a custom made furniture. In this scenario, covering the edge with wooden strips after applying glue might do the trick.
- Plywood is less strong than solid wood.
- Plywood is more costly than fiberboards.
- Furniture made out of plywood has to be manually done thereby taking lots of time.
- Nails are not recommended for plywood for they may cause the material to split. Screws are the best way to fasten the material through proper technique such as drilling.
- Plywood can delaminate in hot climatic regions.
3. Oriented Strand Board

Other terms for Oriented Strand Board are sterling board or flakeboard. This engineered wood is made from compressing flakes with adhesives. OSB is derived from trees which are fast growing and possess a narrow diameter.
Advantages of OSB
- When it comes to price, OSB is less costly than plywood.
- OSB is not only denser than plywood but also stronger.
- OSB can be produced in larger panels compared to plywood.
- OSB can be customized to suit the buyer.
- OSB has nail lines which assist greatly in installation.
Disadvantages of OSB
- When OSB has unprotected edges, it may swell up once exposed to moisture. This happens when cuts are made exposing new unprotected areas.
- The adhesives used in production of the material may emit formaldehyde. Fortunately, it is possible to find manufacturers who produce formaldehyde free materials.
- OSB can be difficult to paint but can still be done. For this exercise, use oil-based paint.
- Once exposed to moisture, plywood is known to swell evenly and dry quicker. This is very unlikely when it comes to OSB as it will take ages to dry.
- OSB is heavier than plywood, this reducing its workability.
Coating
1. Melamine

Initially an organic compound, melamine resin is formed through polymerization as a hard and durable plastic material. It possesses high heat and fire resistance attributes and is commonly applied to particleboard, plywood or MDF. It can be found in a variety of colors, patterns, sizes, and thickness.
Uses
- It is used on cabinets, floors, counters, furniture, and whiteboards.
Advantages
- There is a wide array of melamine colors and patterns to choose from.
- The coating is not only waterproof but also shatter and scratch resistant.
- It offers a concordant finish.
- It is cost friendly in that it is used to cover other wood products.
- It is a lightweight material.
Disadvantages
- As a coating, it is susceptible to chipping.
- In some instances splintering can occur where nails and screws are used.
2. Paper

It is made from acrylic and other types of resins meant to increase the internal bonding strength. Paper coatings are light basis weight papers which are used on surfaces for decorative and protective purposes. They are printed and their top coated with urea, polyester or melamine to enhance durability and performance. They exist in a variety of wood grain patterns and colors for one to choose from.
Uses
- Paper coating is used in cabinetry, home and office furniture, wear- resistant laminate floors, paneling, lamination of chipboard and plywood and other woodwork projects.
Advantages
- They are very easy to clean.
- In comparison to solid wood, they have superior stain and scratch resistant attributes.
- They are affordable.
Disadvantages
- It is not entirely heatproof.
- Unlike natural wood, damaged paper coating cannot be repaired through sanding.
3. Foil

It consists of Layers of paper coated with lacquer or pre-impregnated with acrylic and melamine resins. This results in the formation of a highly impermeable and glossy surface that can be colored or printed on. Lacquer coating is an eco-friendly, hard and protective coating. There are plain wood foils and sheathed foils which are mainly used for coating wood-based products. Varieties in accordance to wood types and style include ash, beech, cherry, walnut and oak.
Uses
It is used on doors, cabinets, furniture and interior designs.
Advantages
- They require low maintenance as the foil resists stains. In addition to this, they are easy to clean.
- Offers many aesthetically pleasing colors and patterns.
- They are waterproof and scratch resistant.
- Foil is not only a durable but also a cost effective material.
Disadvantages
- In cases where foil is not properly installed or maintained, it can peel off.
- Foil is not heat resistant thus should be protected from heat sources.
4. Veneer
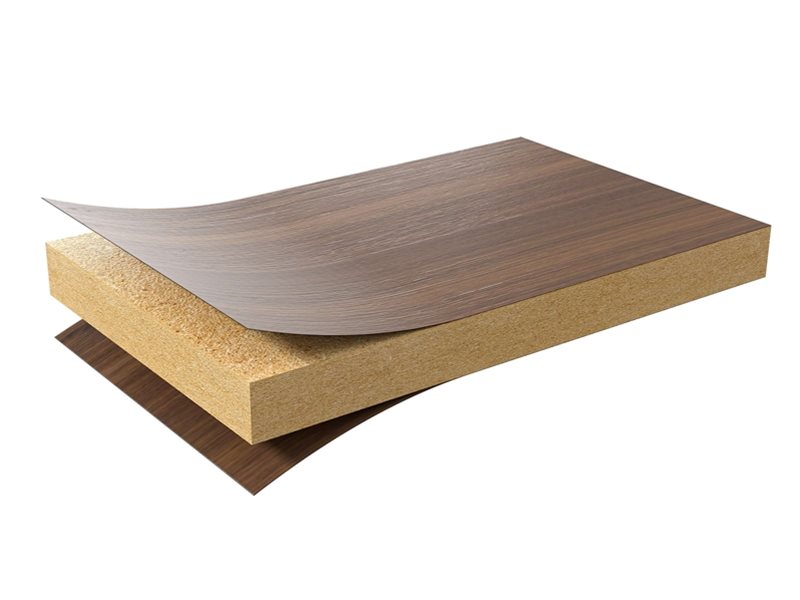


Fine slices of wood which are adhered to wood panels for example MDFs and particle boards to provide a flat panel. Veneer is obtained through slicing of flitches or paring tree trunks through the use of rotary lathes or slicing machines. The grain appearance on veneer depends on the wood species for example mahogany, ebony, and teak. Classes of veneers include phenolic backed, raw, wood on wood, laid up, reconstituted, and paper backed veneers. Veneer can be often differentiated from Solid wood as any carving need to be painted as the natural wood ring on the veneer cannot be pressed onto the carving. Moreover by looking into drilled hole for screws or hinges, we can see whether the inner material is MDF or particle board or solid wood!
Uses
- Adding the appearance of wood to anything for example furniture.
- As a decorative material for wood projects.
- Veneer is also a form of manufactured board
Advantages
- Compared to wood, the occurrences of cracking and splitting are significantly reduced.
- The adhesive used in placing the veneer provides additional strength to the wood.
- Veneers are sustainable as furniture made with veneers use less wood as compared to those made of natural wood only.
- Due to temperature and humidity changes, solid wood may not be ideal in certain projects. Veneers are better alternatives due to their superb expansion and contraction characteristics.
- Veneers provide high quality finishes.
Disadvantages
- Lengthened exposure to moisture can damage the wood veneers.
- To last longer, they will require more maintenance such as polishing and varnishing.
- Wood veneers can’t be repaired once damaged.